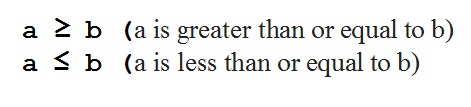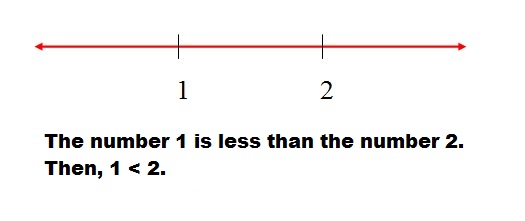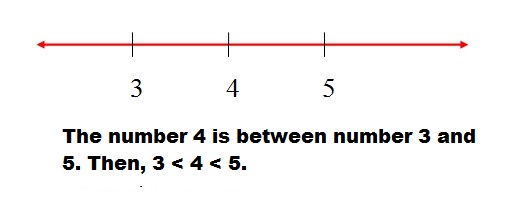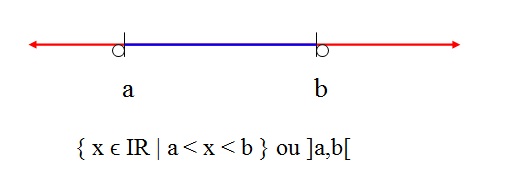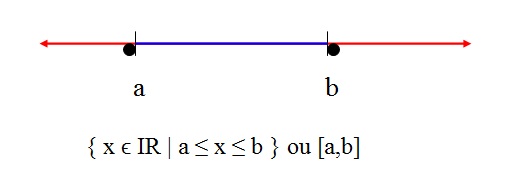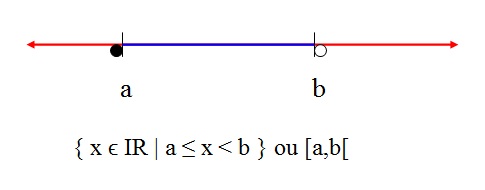Chapter 1
Section 1.7
Ratio of Order in the set of real
Being two real numbers "a" and "b", we have three possibilities of relation of order between them:
1) a = b (a equals ab)
2) a> b (a greater than b)
3) a < b (a less than b)
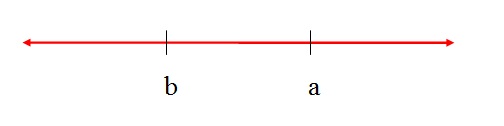
Graphic representation of a > b. If a is greater than b, a is to the right of b in the line of real.
Graphic representation of a < b. If a is less than b, a is to the left of b in the real line.
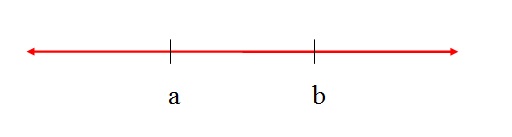
If c > a and c < b, it is represented by a double inequality:
a < c < b
Other forms of relation of order between two real numbers:
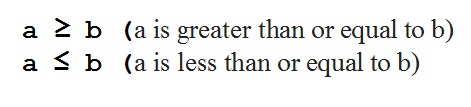
Example:
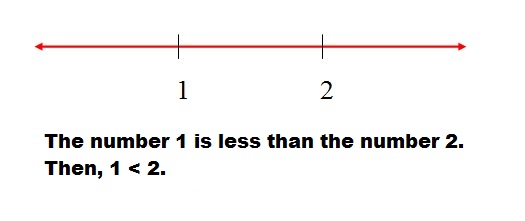
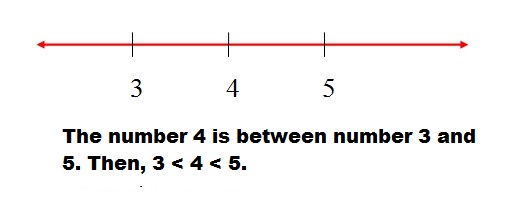
Intervals
Intervals is the name given to the subsets of the reals.
Open interval
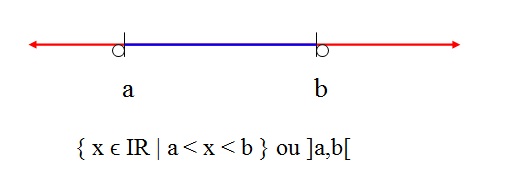
When the ends are represented by empty balls, this means that the numbers a and b do not
belong to the interval.
This interval has all real numbers between a and b.
Closed interval
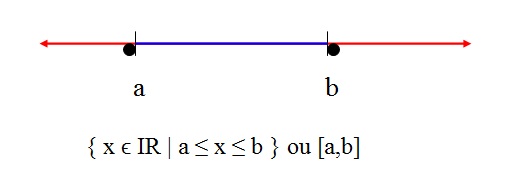
When the ends are represented by full balls, this means that the numbers a and b
belong to the interval.
This interval has all real numbers between a and b, including the a and b themselves
Semi-open interval right
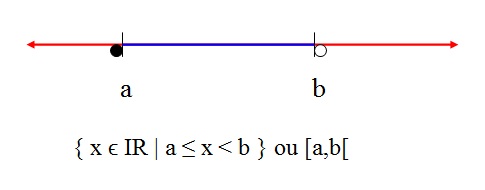
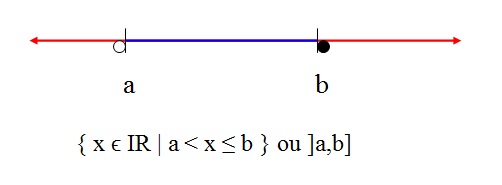
Semi-open interval left
Infinite intervals:
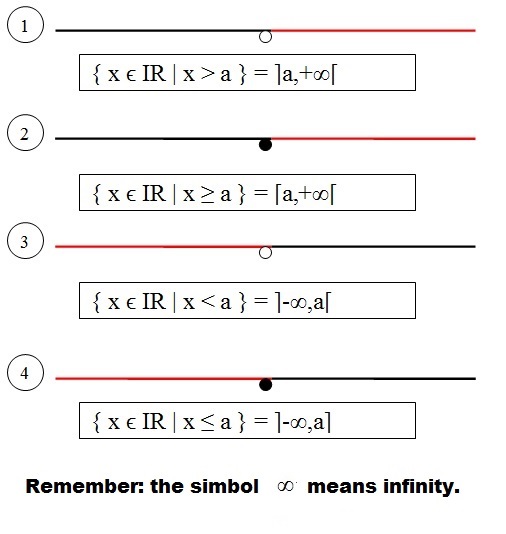
Previous Class
Course Page
Next Class